Attaching wood to metal surfaces may seem challenging, but with the right techniques and tools, it can be a straightforward process. Whether you’re working on a DIY project or professional construction, securing wood to metal is essential for stability and durability.
In this guide, we’ll explore various methods such as using screws, adhesives, and specialized fasteners to create a strong and reliable bond between wood and metal. Discover the best practices and tips to ensure a successful attachment that will withstand the test of time.

Choosing the Right Fastener: Exploring the Best Options for Attaching Wood to Metal
When it comes to joining wood and metal together, choosing the right fastener is crucial for ensuring a strong and secure connection.
Whether you are working on a woodworking project or constructing a metal structure, finding the best fastening option can make all the difference in the durability and stability of your final product. In this section, we will explore some of the top options for attaching wood to metal and discuss their advantages and best use cases.
1. Screws
Screws are one of the most commonly used fasteners for attaching wood to metal. They offer a high level of strength and can provide a secure hold when properly installed.
There are various types of screws available for this purpose, such as self-tapping screws, sheet metal screws, and wood screws with a metal-compatible thread. When choosing screws, it is important to consider factors such as the thickness of the wood and metal, and the load-bearing requirements of the joint.
2. Bolts and Nuts
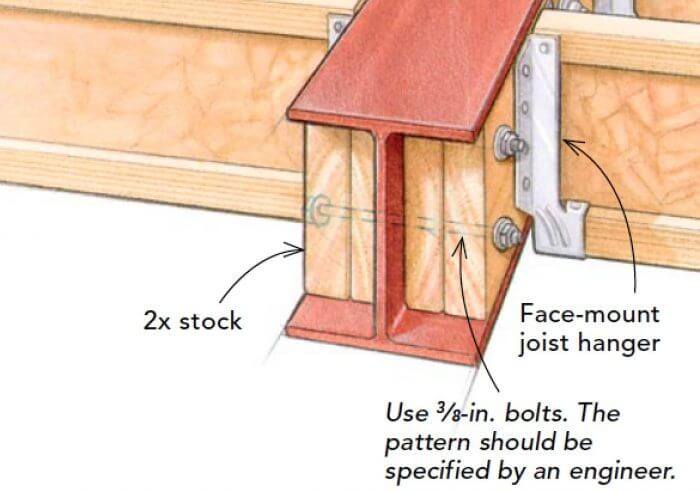
Bolts and nuts are another popular option for attaching wood to metal. They offer excellent strength and can handle heavy loads, making them suitable for structural applications. Bolts are inserted through pre-drilled holes in the wood and metal, and nuts are threaded onto the bolts to secure the connection.
It is important to use washers with bolts to distribute the load evenly and prevent damage to the wood surface.
3. Rivets
Rivets are a type of permanent fastener that can be used to attach wood to metal. They consist of a shaft and a head, and are installed by deforming the shaft to create a secure connection.
Rivets provide a clean and flush finish, making them a popular choice for decorative woodworking projects. However, they are not as strong as screws or bolts and may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.
4. Adhesives
In some cases, using adhesives can be an effective way to attach wood to metal. There are specialized adhesives available that are designed to create a strong bond between these two materials.
Before using adhesives, it is important to ensure that the surfaces are clean, dry, and free from any oils or contaminants. Adhesives can be a good option for lightweight applications or situations where drilling holes may not be desirable.
5. Combination Fasteners
Combination fasteners, also known as hybrid fasteners, are specifically designed for joining wood and metal together. These fasteners typically combine the advantages of screws and bolts, offering a strong and secure connection.
They feature a threaded shaft with a sharp point for easy installation and a bolt-like head for added strength. Combination fasteners can be a versatile option for a wide range of wood-to-metal applications.
6. Anchors
If you need to attach wood to metal in a situation where there are no pre-existing holes, anchors can be a viable solution. Anchors are typically used in masonry or concrete applications, but there are specialized anchors available for attaching wood to metal.
These anchors are inserted into pre-drilled holes in the wood and metal and provide a secure hold. They are especially useful when working with thin metal sheets.
When it comes to attaching wood to metal, choosing the right fastener is essential for a strong and secure connection. Screws, bolts and nuts, rivets, adhesives, combination fasteners, and anchors are all viable options, each with their own advantages and best use cases.
Consider the specific requirements of your project, such as load-bearing capacity and the desired finish, to determine which fastening option is the most suitable.
Screw vs. Nail: Which Fastener is Suitable for Joining Wood and Metal?
When it comes to joining wood and metal, choosing the right fastener is crucial for a strong and durable bond. Two popular options for this purpose are screws and nails. While both serve the same purpose of joining materials together, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
Screw
A screw is a threaded fastener that is commonly used for joining wood and metal. It consists of a pointed tip, helical threads, and a head. The threads on a screw provide excellent grip and hold, making it ideal for applications where a strong connection is required. The threaded design allows the screw to dig into the material, creating a secure bond.
One of the key advantages of screws is their ability to be easily removed and reinserted without damaging the materials. This makes them a preferred choice for projects that may require disassembly or adjustments.
Additionally, screws offer better resistance to pulling forces, making them suitable for applications where the joint may be subjected to considerable stress.
There are different types of screws available, including wood screws, self-tapping screws, and machine screws.
Wood screws are designed specifically for use in wood and are available in various lengths and diameters. Self-tapping screws have a sharp tip that allows them to create their threads as they are driven into the material. Machine screws, on the other hand, are typically used in conjunction with a nut or threaded insert.
Nail
A nail is a cylindrical metal pin with a flat head that is hammered into materials to join them together. Nails are commonly used in carpentry and construction projects due to their ease of use and cost-effectiveness. They provide a quick and efficient way to secure materials, especially in applications where speed is essential.
Nails rely on friction and shear strength to hold materials in place. The tapered design of the nail allows it to penetrate the wood or metal, creating a tight fit.
However, nails do not offer the same level of holding power as screws, especially when it comes to resisting pulling forces. Therefore, they are more suitable for applications where the joint will not be subjected to significant stress.
There are various types of nails available, including common nails, finishing nails, and brad nails. Common nails are heavy-duty nails that are commonly used in structural applications.
Finishing nails have a smaller head and are designed to be less noticeable once driven in. Brad nails are even smaller and are typically used for attaching delicate moldings and trim.
Choosing the Right Fastener
When deciding between screws and nails for joining wood and metal, several factors should be considered. The intended application, the materials being joined, and the level of strength required are all important considerations.
If you need a strong and secure connection that can withstand pulling forces, screws are the better choice. They provide excellent grip and can be easily removed if necessary. Screws are particularly suitable for projects where disassembly or adjustment may be needed.
On the other hand, nails are more suitable for applications where speed and cost-efficiency are important factors. They are quick to install and are less expensive than screws. Nails are commonly used in projects where the joint will not be subjected to significant stress.
In summary, both screws and nails have their advantages and are suitable for different applications. Choosing the right fastener depends on factors such as the intended use, materials, and strength requirements. By understanding the characteristics of screws and nails, you can make an informed decision and ensure a strong and reliable joint between wood and metal.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Securely Attach Wood to Metal
If you’re working on a project that involves joining wood and metal together, it’s important to ensure a secure and durable connection.
Whether you’re building furniture, framing walls, or constructing outdoor structures, attaching wood to metal properly is essential for the structural integrity of your project. In this section, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to securely attach wood to metal.
1. Gather the Necessary Tools and Materials
Before you start the attachment process, gather all the necessary tools and materials. This will ensure a smooth workflow and prevent any interruptions. Here’s a list of items you’ll need:
- Wood screws or bolts
- Drill
- Drill bits
- Wrench or socket set
- Clamps or vise grips
- Protective eyewear and gloves
2. Mark the Attachment Points
Once you have all your tools and materials ready, the next step is to mark the attachment points on both the wood and metal surfaces. Use a pencil or marker to clearly indicate where the screws or bolts will go.
3. Pre-drill the Holes
Pre-drilling the holes is crucial, as it helps prevent the wood from splitting and ensures a clean and precise attachment. Use a drill bit that matches the size of your screws or bolts to create pilot holes in both the wood and metal surfaces.
4. Align the Wood and Metal
After pre-drilling the holes, align the wood and metal pieces together at the marked attachment points. Make sure they are positioned correctly and check for any gaps or misalignments.
5. Secure the Wood to the Metal
Depending on your project and the materials you’re working with, you can choose to use wood screws or bolts for the attachment. If using wood screws, insert them into the pre-drilled holes and use a drill or screwdriver to tighten them. If using bolts, insert them through the holes and secure them with nuts using a wrench or socket set.
6. Check the Stability and Alignment
Once the wood is securely attached to the metal, check the stability and alignment of the connection. Apply pressure or gently shake the joint to ensure it’s solid and doesn’t move or wobble. If needed, make any adjustments or tighten the screws/bolts further.
7. Test the Attachment
Before considering the attachment complete, it’s important to test its strength and durability. Depending on your project, apply force or pressure to the joint to simulate real-world conditions. This will help ensure that the wood and metal connection can withstand the intended use.
8. Finish and Protect the Connection (Optional)
If desired, you can finish and protect the wood and metal connection. Apply a coat of paint or a protective finish to prevent corrosion, rust, or other potential damage over time. This step is particularly important if your project is exposed to outdoor elements.
Summary
Attaching wood to metal securely requires careful planning, precise execution, and the right tools. By following this step-by-step guide, you can ensure a strong and reliable connection between the two materials.
Remember to gather all the necessary tools, mark the attachment points, pre-drill the holes, align the wood and metal, and secure them using appropriate screws or bolts. Test the attachment for stability and durability, and consider adding a protective finish if needed. With these steps, you can confidently attach wood to metal in your projects.
Precautions and Tips for Attaching Wood to Metal: Ensuring Durability and Safety
Attaching wood to metal is a common practice in many construction and DIY projects. Whether you’re building furniture, installing shelves, or constructing a deck, it’s important to ensure that the wood is securely fastened to the metal for both durability and safety. Here are some precautions and tips to follow when attaching wood to metal:
1. Choose the Right Fasteners
Using the right fasteners is crucial for a strong and long-lasting connection between wood and metal. When selecting screws or bolts, make sure they are specifically designed for wood-to-metal applications. These fasteners are usually coated or treated to prevent corrosion, ensuring the integrity of the joint over time.
2. Use Pre-Drilled Holes
Before attaching the wood to the metal, it’s important to pre-drill pilot holes. This will prevent the wood from splitting and make it easier to drive the fasteners into the metal. The diameter of the pilot hole should be slightly smaller than the diameter of the fastener to ensure a secure fit.
3. Consider the Thickness of the Material
Take into account the thickness of both the wood and the metal when choosing the length of the fasteners. The fasteners should be long enough to penetrate both materials without protruding too much. If the fasteners are too short, they may not provide enough strength, while if they are too long, they can pose a safety hazard.
4. Use Washers or Spacers
When attaching wood to metal, using washers or spacers can help distribute the load and prevent the wood from coming into direct contact with the metal. This can reduce the risk of corrosion and ensure a more secure attachment. Place a washer or spacer between the wood and the metal before driving in the fastener.
5. Consider the Environment
Before attaching wood to metal, consider the environment in which the joint will be exposed. If there is a risk of moisture or humidity, it’s important to use fasteners and materials that are resistant to corrosion. Stainless steel or galvanized fasteners are often recommended for outdoor or high-moisture applications.
6. Maintain Proper Distance
When attaching wood to metal, it’s important to maintain a proper distance between the fasteners. This will help distribute the load evenly across the joint and prevent any weak points. As a general rule of thumb, aim for a spacing of approximately 6 to 8 inches between fasteners, depending on the size and weight of the wood.
7. Regularly Inspect the Joint
After attaching the wood to metal, regularly inspect the joint for any signs of loosening or wear. Over time, the vibrations and movements can cause fasteners to become loose. It’s important to tighten any loose fasteners promptly to ensure the integrity and safety of the connection.
By following these precautions and tips, you can ensure that your wood-to-metal attachments are durable and safe. Remember to choose the right fasteners, use pre-drilled holes, consider the thickness of the materials, use washers or spacers, consider the environment, maintain proper distance between fasteners, and regularly inspect the joint.
With proper installation and maintenance, your wood-to-metal attachments will withstand the test of time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Attaching Wood to Metal
Attaching wood to metal can be a tricky task, especially if you are not familiar with the correct techniques.
Whether you are working on a DIY project or a professional construction job, it is important to avoid common mistakes that can compromise the strength and durability of the attachment. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common mistakes to avoid when attaching wood to metal.
1. Not Using the Right Fasteners
Using the correct fasteners is crucial when attaching wood to metal. Many people make the common mistake of using ordinary screws or nails that are not suitable for this type of connection.
When attaching wood to metal, it is important to use self-drilling screws or bolts that are specifically designed for this purpose. These fasteners have a sharp point and special threads that can penetrate and grip the metal securely.
2. Ignoring the Protective Barrier
Another common mistake is ignoring the need for a protective barrier between the wood and the metal. Direct contact between the two materials can lead to corrosion, weakening the attachment over time.
To prevent this, it is essential to use a barrier such as a plastic or rubber washer, or a corrosion-resistant coating on the metal surface. This barrier will create a separation between the wood and the metal, ensuring longevity and strength.
3. Overlooking Pre-drilling
Pre-drilling is an important step that is often overlooked when attaching wood to metal. It involves creating pilot holes in the wood to guide the fasteners. By pre-drilling, you can prevent the wood from splitting or cracking when the fasteners are driven in.
It also allows for easy and accurate alignment of the wood and metal components. Ignoring pre-drilling can result in a weak attachment and compromised structural integrity.
4. Improper Alignment
Proper alignment is essential for a strong and secure attachment between wood and metal. One common mistake is not ensuring that the wood and metal components are perfectly aligned before driving in the fasteners.
Misalignment can result in uneven stress distribution and weakens the connection over time. It is crucial to take the time to align the components accurately to achieve a sturdy and reliable attachment.
5. Lack of Structural Support
When attaching wood to metal, it is important to consider the need for additional structural support. Depending on the load or weight that the attachment will bear, you may need to add additional support such as brackets or reinforcements.
Neglecting to provide adequate support can lead to sagging, bending, or even failure of the attachment under excessive load or stress. Always assess the structural requirements and ensure sufficient support is in place.
In summary, attaching wood to metal requires careful attention to detail and adherence to proper techniques.
By avoiding common mistakes such as using improper fasteners, neglecting the protective barrier, overlooking pre-drilling, improper alignment, and lack of structural support, you can ensure a strong and durable attachment. Taking the time to do it right will result in a reliable and long-lasting connection between wood and metal.
FAQs
Q: How can I attach wood to metal?
There are a few methods you can use to attach wood to metal. One option is to use self-tapping screws designed for wood and metal. Pre-drill holes in the wood, then screw them into the metal. Another method is to use construction adhesive specifically designed for bonding wood to metal surfaces.
Q: Can I use nails to attach wood to metal?
Nails are generally not recommended for attaching wood to metal, as they may not provide a secure enough connection. However, if you have a specific situation where nails are necessary, you can use specialized nails, such as masonry nails or hardened steel nails, and pre-drill holes in the wood and metal to prevent splitting.
Q: Are there any other options for attaching wood to metal?
Yes, another option is to use metal brackets or angle brackets. These brackets are designed to provide a strong and secure connection between wood and metal. Simply attach the brackets to the wood and metal using screws or bolts, ensuring that they are properly aligned and tightened.
Conclusion
In conclusion, attaching wood to metal can be achieved using several effective methods. One popular approach is using screws or bolts specifically designed for wood-to-metal connections. These fasteners provide a secure and durable attachment, ensuring the wood and metal stay firmly together.
Another method involves utilizing adhesives formulated for bonding wood and metal surfaces. These adhesives create a strong bond, eliminating the need for mechanical fasteners.
Additionally, using brackets, angle irons, or metal connectors can provide extra stability and support when attaching wood to metal. Whichever method you choose, it’s essential to ensure proper alignment, pre-drilling, and surface preparation for a successful and long-lasting connection.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently and effectively attach wood to metal for various projects, such as furniture construction, home renovations, or DIY crafts. Remember to tailor your approach based on the specific requirements and load-bearing capacity of the joint to ensure a secure and reliable attachment.