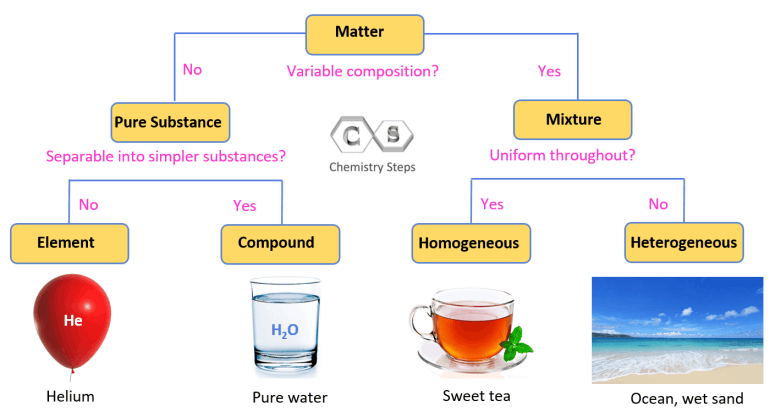
Wood is not considered a pure substance. Rather, it is a complex mixture of different compounds, including cellulose, lignin, and various organic materials. It is a natural material that comes from trees and is used extensively in construction, furniture making, and other applications.
The composition of wood can vary depending on the type of tree it comes from, as well as factors such as age and growing conditions. This variability gives wood its unique characteristics and makes it a versatile material with a wide range of uses.

Although wood is not a pure substance, it is still a valuable resource that has been used by humans for thousands of years. Its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal make it a popular choice in many industries.
Overall, while wood may not meet the definition of a pure substance, it remains an essential and valuable material that plays a crucial role in our daily lives.

Types of Wood: A Guide to Different Varieties
Wood is a versatile and widely-used material that has been utilized by humans for thousands of years. From construction to furniture making, woodworking projects to art, the type of wood you choose plays a significant role in the outcome of your project. In this section, we will explore different varieties of wood, their characteristics, and the best applications for each type.
1. Softwood
Softwood is derived from coniferous trees, which are typically evergreen and bear cones. It is the most commonly used type of wood and is known for its affordability, availability, and versatility. Some popular types of softwood include:
- Pine: Pine is a light-colored wood that is relatively soft and easy to work with. It is commonly used for interior projects such as furniture, paneling, and trim.
- Spruce: Spruce is a pale wood that is lightweight and easily sourced. It is often used in construction, as well as for making musical instruments.
- Cedar: Cedar is a durable and rot-resistant wood with a distinct aroma. It is commonly used for outdoor projects such as fencing, decking, and siding.
2. Hardwood
Hardwood comes from deciduous trees that lose their leaves annually. It is known for its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. While hardwood is generally more expensive than softwood, it is often considered a premium material. Some popular types of hardwood include:
- Oak: Oak is a dense and durable wood that is prized for its distinctive grain. It is commonly used in furniture, flooring, and cabinetry.
- Maple: Maple is a light-colored wood that is highly resistant to wear and tear. It is often used for kitchen cabinets, cutting boards, and decorative veneers.
- Cherry: Cherry wood is known for its rich tones and smooth finish. It is commonly used in high-end furniture, cabinetry, and millwork.
3. Exotic Wood
Exotic woods come from trees that are native to regions outside of North America and Europe. They offer unique colors, patterns, and textures, making them highly sought after for specialty woodworking projects. Some popular types of exotic wood include:
- Teak: Teak is a durable and water-resistant wood that is commonly used in outdoor furniture, boat building, and decking.
- Ebony: Ebony is a dense and dark-colored wood that is often used in musical instruments, fine furniture, and luxury items.
- Mahogany: Mahogany is a reddish-brown wood that is prized for its beauty and workability. It is commonly used in high-quality furniture and cabinetry.
4. Engineered Wood
Engineered wood, also known as composite wood, is made by binding together strands, particles, fibers, or veneers of wood with adhesive. It offers the advantages of strength, dimensional stability, and consistency. Some popular types of engineered wood include:
- Plywood: Plywood is made by gluing together multiple layers of thin wood veneers. It is commonly used in construction, furniture, and cabinetry.
- MDF: Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) is made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibers and combining them with wax and resin. It is often used for furniture, shelving, and moldings.
- Particleboard: Particleboard is made by pressing wood particles with adhesive under high pressure and temperature. It is commonly used for shelving, cabinets, and furniture.
Choosing the right type of wood for your project is essential for achieving the desired outcome. Consider the characteristics, availability, and intended use of the wood before making a decision. Whether you’re a woodworking enthusiast or a professional carpenter, understanding the different varieties of wood will enhance your craftsmanship and ensure the success of your projects.
Properties of Wood: Strength, Density, and Durability
Wood is one of the oldest and most commonly used building materials in the world. Its unique properties make it a versatile choice for a wide range of applications, from furniture and flooring to structural components in buildings. Understanding the properties of wood, particularly its strength, density, and durability, is essential for selecting the right type of wood for a specific project.
Strength
The strength of wood refers to its ability to withstand external forces and resist deformation or breakage. It is an important consideration when choosing wood for load-bearing structures or any application that requires structural integrity. Wood strength is influenced by several factors, including the species of wood, its moisture content, and its grain orientation.
Various tests are conducted to determine the strength of wood, such as bending tests, compression tests, and tensile tests. These tests measure the wood’s resistance to bending, compression, and tension forces, respectively. The results of these tests are usually expressed in terms of modulus of elasticity, modulus of rupture, and compressive/tensile strength.
Density
Density is a measure of the mass of wood per unit volume. It plays a significant role in determining the weight and overall performance of wooden structures. Wood with higher density tends to be stronger and more durable than wood with lower density.
Density also affects the wood’s ability to absorb moisture and resist decay. Denser woods have a lower moisture absorption rate and are less prone to fungal or insect attacks. However, denser woods can be more challenging to work with and may require specialized tools and techniques.
Durability
Durability refers to the ability of wood to withstand environmental factors, such as moisture, temperature changes, and biological degradation. It is a critical consideration for outdoor applications or areas with high moisture content, such as kitchens and bathrooms.
The durability of wood depends on its natural resistance to decay and its susceptibility to insect damage. Some wood species, such as cedar and teak, are naturally more durable due to their inherent chemical properties. Additionally, wood preservatives can be used to enhance the durability of certain wood species.
The durability of wood is usually classified into different durability classes, ranging from very durable to non-durable. This classification helps in selecting the appropriate wood species for specific applications, ensuring long-term performance and minimizing maintenance requirements.
In summary, understanding the properties of wood, including its strength, density, and durability, is crucial for making informed decisions when choosing wood for various applications. Strength determines the wood’s ability to withstand external forces, density affects its weight and resistance to moisture and decay, and durability ensures its long-term performance. By considering these properties, one can select the most suitable wood type for a specific project, ensuring both functionality and aesthetics.

Manufacturing Process: From Tree to Timber
In this section, we will explore the fascinating journey of how trees are transformed into timber, a versatile building material that is widely used in construction and various other industries.
The manufacturing process of timber involves several steps, each contributing to the quality and characteristics of the final product. Let’s delve into the details of this intricate process:
1. Harvesting and Transportation:
The first step in the manufacturing process is the harvesting of trees. This process involves carefully selecting mature trees for felling, ensuring sustainable forestry practices are followed. Once the trees are cut down, they are transported to sawmills for further processing.
2. Sawmilling:
At the sawmill, the harvested logs are debarked to remove the outer layer of the tree. This is done to eliminate dirt, insects, and any other impurities that may be present. The debarked logs are then cut into desired lengths and sizes using specialized sawing machines.
3. Drying or Seasoning:
To enhance the stability and durability of the timber, it undergoes a drying or seasoning process. This process involves reducing the moisture content of the wood to a suitable level. There are two primary methods of drying timber: air drying and kiln drying.
In air drying, the timber is stacked in a well-ventilated area and left to dry naturally over a period of months or even years. Kiln drying, on the other hand, involves placing the timber in large chambers where controlled heat, humidity, and airflow are used to accelerate the drying process.
4. Planing and Finishing:
Once the timber has been dried, it is planed to achieve a smooth and even surface. This process removes any irregularities, such as rough spots or uneven edges, resulting in a more polished appearance.
Additionally, timber may undergo additional finishing processes, such as sanding, staining, or coating, to enhance its aesthetics and protect it from environmental factors.
5. Grading and Sorting:
After the timber has been processed and finished, it undergoes a grading and sorting process. This step involves assessing the quality of the timber based on various factors, including its appearance, strength, and structural integrity.
Timber is typically graded according to industry standards, such as the National Grading Rule, which categorizes the wood based on its intended use and quality. This ensures that the right type of timber is used for specific applications, such as construction, furniture making, or flooring.
6. Distribution and Utilization:
Once the timber has been graded and sorted, it is ready for distribution and utilization. It is transported to various industries and construction sites where it is used for a wide range of purposes.
Timber is a versatile material that can be used for structural purposes, such as beams, columns, and trusses, as well as for decorative elements, furniture, flooring, and many other applications. Its natural strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal make it a preferred choice for many architects, builders, and designers.
7. Environmental Considerations:
It is important to note that sustainable forestry practices and proper forest management play a crucial role in ensuring a responsible manufacturing process from tree to timber. Forest certification systems, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), promote responsible sourcing and production of timber, ensuring that it comes from well-managed forests.
In summary, the manufacturing process of timber involves the careful harvesting, transportation, sawmilling, drying, planing, finishing, grading, and utilization of trees. This process ensures that the final product meets quality standards and is suitable for a wide range of applications. By following sustainable practices, we can ensure the availability of timber as a renewable and environmentally-friendly building material.
Common Uses of Wood in Construction and Design
Wood is a versatile and widely used material in construction and design. Its natural beauty, durability, and sustainability make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications. In this section, we will explore some of the common uses of wood in construction and design.
1. Structural Support
One of the primary uses of wood in construction is for structural support. Wood is an excellent choice for building frameworks, such as walls, floors, roofs, and beams. Its strength-to-weight ratio allows it to provide stable and reliable support for buildings of various sizes and shapes.
Wooden beams and columns are often used in traditional and modern architecture to create open floor plans and unique designs. The natural warmth and character of wood also add a touch of elegance to the structural elements of a building.
2. Exterior Cladding
Wooden exterior cladding is a popular choice for both residential and commercial buildings. It offers a natural and timeless look that can enhance the aesthetic appeal of any structure. Wood cladding is available in various species and finishes, allowing architects and designers to create a wide range of styles and patterns.
In addition to enhancing the visual appeal, wood cladding also provides protection against weather elements. It acts as a barrier, preventing moisture from penetrating the building and helping to insulate the interior spaces.
3. Interior Finishes
Wood is widely used for interior finishes, including flooring, wall paneling, and cabinetry. Hardwood floors, for example, are durable, easy to clean, and offer a timeless look. They can add warmth and character to any room, creating a welcoming and comfortable atmosphere.
Wooden wall paneling is another popular choice for interior design. It can add texture, depth, and richness to a space, creating a focal point or accentuating certain areas. Additionally, wood cabinetry and furniture are often preferred for their natural beauty and durability.
4. Furniture and Decor
Wood is a popular material for furniture and decor due to its natural beauty and versatility. From dining tables and chairs to bookshelves and bedside tables, wooden furniture adds a touch of elegance and warmth to any interior space.
Wood is also commonly used for decorative elements, such as staircases, handrails, trim work, and crown moldings. These details can enhance the overall design aesthetic and create a cohesive and harmonious look.
5. Landscaping and Outdoor Structures
Wood is extensively used in landscaping and the construction of outdoor structures. It is commonly used for decking, pergolas, fences, and garden structures. Wood decking provides a natural and durable surface for outdoor living areas, while pergolas and fences add privacy and create a visually appealing outdoor space.
Additionally, wood is often used for the construction of bridges, boardwalks, and gazebos in parks and recreational areas. Its natural beauty blends well with the surrounding environment, creating a seamless connection between nature and man-made structures.
6. Renewable Energy
Wood is also used in the production of renewable energy. It is widely used as a biomass fuel for heating and power generation. Wood pellets, chips, and logs are burned in biomass boilers and power plants to produce heat and electricity. This sustainable energy source helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels and contributes to a greener and more environmentally friendly future.
In summary, wood is a versatile and sustainable material that finds a wide range of applications in construction and design. Its strength, beauty, and durability make it an ideal choice for structural support, exterior cladding, interior finishes, furniture and decor, landscaping, outdoor structures, and even renewable energy production.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Wood Products
Wood products have long been utilized for various purposes due to their versatility, durability, and aesthetic appeal. However, in recent years, there has been an increasing concern about the sustainability and environmental impact of using wood as a resource. This section explores the key aspects of sustainability and the environmental implications associated with wood products.
1. Sustainable Forestry Practices
One of the primary concerns regarding wood products is the depletion of forests and the impact on biodiversity. To address this, sustainable forestry practices have emerged, aiming to ensure the long-term availability of wood resources while minimizing negative environmental effects. Sustainable forestry involves practices such as:
- Implementing selective logging techniques to minimize damage to surrounding trees and habitats.
- Promoting reforestation and afforestation efforts to replace harvested trees and maintain healthy forest ecosystems.
- Adopting responsible forest management plans that consider ecological, social, and economic aspects.
These practices help maintain the balance between wood production and the preservation of forests, ensuring a sustainable supply of wood for future generations.
2. Carbon Footprint
Wood products have a relatively low carbon footprint compared to alternative materials such as steel or concrete. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, acting as carbon sinks. When wood is harvested and used in products, it continues to store carbon, preventing it from being released back into the atmosphere.
Using wood as a construction material in place of other options can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Wood also requires less energy to manufacture and transport, further reducing its environmental impact.
3. Life Cycle Assessment
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a comprehensive method used to evaluate the environmental impact of products throughout their entire life cycle. This assessment considers all stages, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, product use, and end-of-life disposal.
LCA studies have shown that wood products have favorable environmental performance compared to alternatives. Wood has a lower energy demand and significantly reduces the emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases.
4. Forest Certification and Chain of Custody
Forest certification systems, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC), provide assurance that wood products come from well-managed and sustainable sources. These certifications ensure that the wood has been harvested legally, promotes responsible forest management, and protects indigenous people’s rights.
Chain of Custody (CoC) certification tracks the flow of wood products from the forest to the end consumer, ensuring that certified wood is properly identified and separated from non-certified sources.
5. Wood Waste Management
Efficient wood waste management is crucial to reduce the environmental impact associated with wood processing and manufacturing. It involves practices such as:
- Recycling wood waste for use in other industries, such as energy generation or composite materials.
- Implementing proper waste disposal methods to prevent pollution of water and soil.
- Promoting the use of by-products and residues from wood processing to minimize waste.
By maximizing the utilization of wood resources and minimizing waste, the environmental impact can be significantly reduced.
Summary
Wood products can be sustainable and have a low environmental impact when sourced and managed responsibly. Sustainable forestry practices, carbon sequestration, life cycle assessments, forest certification, chain of custody, and efficient wood waste management are key aspects that contribute to the sustainability of wood products. By ensuring these practices are followed, wood remains a valuable and eco-friendly material for various applications.
FAQs
Is wood a pure substance?
No, wood is not a pure substance. It is a complex mixture of various components such as cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and extractives. These components give wood its unique properties and characteristics.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, wood is not considered a pure substance. It is a complex and heterogeneous material composed of various organic compounds, such as cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose. These components give wood its unique properties, including strength, durability, and workability. The presence of different chemical structures and compositions results in variations in color, density, and texture among different types of wood. Therefore, wood can be classified as a mixture rather than a pure substance. Its diverse nature makes it a valuable resource for construction, furniture making, and artistic craftsmanship.