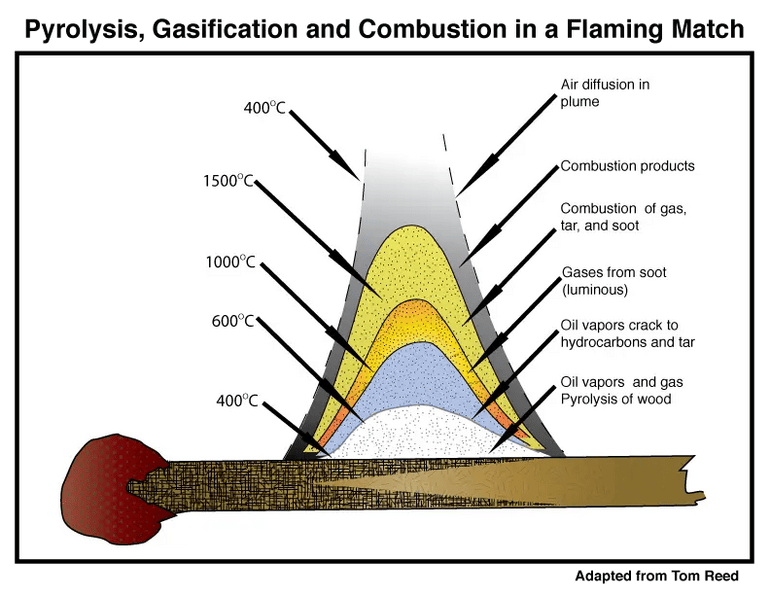
Wood combustion occurs when the temperature reaches a specific point, known as the ignition temperature. The ignition temperature of wood can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of wood and its moisture content. Generally, the ignition temperature for most woods ranges between 300 to 500 degrees Celsius (572 to 932 degrees Fahrenheit). When exposed to these high temperatures, wood undergoes combustion, releasing heat energy and producing flames and smoke.
Factors Affecting Wood Combustion Temperature: Moisture Content, Density, and Species
When it comes to wood combustion, several factors play a significant role in determining the temperature at which wood burns. These factors include moisture content, density, and the species of the wood. Understanding how these factors influence wood combustion can help optimize the burning process and improve overall efficiency.
1. Moisture Content
Moisture content is perhaps the most crucial factor affecting wood combustion temperature. Wood naturally contains moisture, which can significantly impact its burning characteristics. When wood is freshly cut, it typically has a high moisture content, making it difficult to burn efficiently.
High moisture content in wood results in incomplete combustion and lower temperatures. This is because a significant amount of energy is used to evaporate the moisture before the wood can catch fire. As a result, wet or green wood tends to produce more smoke and less heat compared to dry wood.
On the other hand, seasoned or properly dried wood has a lower moisture content, making it easier to ignite and burn at higher temperatures. Dry wood burns more efficiently, producing more heat and less smoke. It is worth noting that the ideal moisture content for burning wood efficiently is typically below 20%.
2. Density
The density of wood also affects its combustion temperature. Wood with higher density tends to burn at higher temperatures compared to less dense wood. This is due to the fact that denser wood contains more energy per unit volume, allowing for a more intense and hotter combustion process.
Hardwood species, such as oak or maple, generally have higher densities and therefore burn at higher temperatures. Softwood species, like pine or spruce, have lower densities and tend to burn at lower temperatures. It is important to consider the density of the wood when determining its suitability for specific applications or heating purposes.
3. Species
The species of wood also plays a role in determining its combustion temperature. Different wood species have varying chemical compositions, which can influence their combustion characteristics. Some species are known to burn hotter and more efficiently than others.
For example, hardwood species like hickory or cherry are highly prized for their ability to produce intense heat and long-lasting fires. Softwood species, such as cedar or fir, may burn at lower temperatures but are often preferred for their quick ignition and aromatic properties.
It is important to note that the combustion temperature of wood species can also be influenced by factors such as moisture content and density. The ideal choice of wood species for burning will depend on the specific requirements and preferences of the user.
Summary
In summary, the combustion temperature of wood is influenced by several factors, including moisture content, density, and species. Moisture content significantly affects the efficiency of combustion, with lower moisture content leading to higher temperatures and more efficient burning. Density plays a role in determining the intensity of the combustion process, with denser wood burning at higher temperatures. Lastly, different wood species have varying combustion characteristics, with some species known for their high heat output and others valued for their quick ignition. By understanding these factors, individuals can make informed choices when selecting wood for their desired purposes.

Dangerous Wood Combustion Temperatures: Identifying the Risks
Wood combustion is a common method of heating and cooking in many households. However, it is important to understand that wood can reach dangerous temperatures during the combustion process, posing various risks. In this section, we will explore these risks and highlight the importance of identifying and mitigating them.
1. Structural Fire Hazards
One of the primary risks associated with wood combustion is the potential for structural fires. When wood burns at high temperatures, it can ignite nearby flammable materials, such as curtains, furniture, or even other wooden structures, leading to a devastating fire. These fires can spread rapidly, endangering lives and causing extensive property damage.
To mitigate the risk of structural fires, it is crucial to maintain a safe distance between the wood-burning stove or fireplace and any flammable materials. Installing heat-resistant barriers, such as fire-resistant glass or metal screens, can also provide an additional layer of protection. Regular inspection and cleaning of chimneys and flue pipes can prevent the buildup of flammable creosote, reducing the risk of chimney fires.
2. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Another significant risk associated with wood combustion is the release of carbon monoxide (CO) gas. CO is a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly when inhaled in high concentrations. Improper combustion or inadequate ventilation can lead to the buildup of CO indoors, resulting in carbon monoxide poisoning.
It is crucial to ensure proper ventilation when using wood-burning appliances. This includes having a well-functioning chimney or flue system that allows for the efficient removal of combustion byproducts, including CO. Installing carbon monoxide detectors in areas where wood combustion is performed can provide an early warning system in case of elevated CO levels.
3. Health Risks from Fine Particulate Matter
Wood combustion releases fine particulate matter (PM) into the air. These particles can be inhaled and pose various health risks, particularly to individuals with respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Fine PM can irritate the respiratory system, leading to breathing difficulties, coughing, and exacerbation of existing conditions.
To minimize the health risks associated with fine particulate matter, it is essential to use wood-burning appliances that meet emission standards and have efficient combustion processes. Additionally, maintaining proper ventilation and ensuring adequate air circulation can help reduce the concentration of PM indoors.
4. Environmental Impact
Wood combustion also has environmental consequences. The release of pollutants, including carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributes to air pollution and climate change. Inefficient wood-burning appliances and the use of unseasoned or improperly seasoned wood can significantly increase these emissions.
To minimize the environmental impact of wood combustion, it is important to choose EPA-certified wood-burning appliances that are designed for efficient combustion and low emissions. Using properly seasoned wood with a moisture content of around 20% or less can also help reduce emissions. Additionally, exploring alternative heating options, such as pellet stoves or electric heaters, can further reduce the environmental footprint.
Summary
Wood combustion can reach dangerous temperatures, posing various risks. The primary risks include structural fire hazards, carbon monoxide poisoning, health risks from fine particulate matter, and environmental impact. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to maintain a safe distance from flammable materials, ensure proper ventilation, and use efficient wood-burning appliances. Regular inspection and cleaning of chimneys, installation of carbon monoxide detectors, and proper wood seasoning are essential preventive measures. By being aware of the risks associated with wood combustion and taking appropriate precautions, we can ensure a safer and healthier environment.

Preventing Wood Combustion: Fire Safety Measures and Precautions
Wood combustion is a common cause of fires in both residential and commercial settings. These fires can cause significant damage to property and even lead to loss of life. It is crucial to implement fire safety measures and precautions to prevent wood combustion incidents from occurring. In this section, we will discuss some effective strategies for fire prevention and highlight the importance of fire safety.
1. Proper Storage and Handling of Wood
One of the primary factors contributing to wood combustion is improper storage and handling. It is essential to store wood in a safe and designated area, away from potential ignition sources. Wood should be stacked neatly with sufficient spacing to allow for proper airflow and prevent the buildup of heat. Avoid storing excessive amounts of wood indoors, as it can create a fire hazard. Regularly inspect the wood storage area for any signs of damage or deterioration and promptly address any issues.
2. Installation of Fire-Resistant Materials
Utilizing fire-resistant materials in the construction of buildings can significantly reduce the risk of wood combustion. Consider using fire-resistant paint, treated fire-resistant wood, or flame-retardant coatings to enhance the fire resistance of wooden structures. These materials can slow down the spread of fire and provide valuable time for evacuation and fire suppression.
3. Proper Maintenance and Inspection
Maintaining and inspecting your wood-burning appliances and heating systems is crucial for fire prevention. Regularly clean chimneys, flues, and vents to remove creosote buildup, which can ignite and cause a fire. Ensure that all wood-burning appliances are installed and maintained correctly, following manufacturer guidelines. It is also essential to have routine inspections conducted by professionals to identify and address any potential fire hazards.
4. Installation of Smoke Alarms and Fire Suppression Systems
Smoke alarms and fire suppression systems are vital tools for early detection and suppression of fires caused by wood combustion. Install smoke alarms in every room, ensuring they are interconnected and have working batteries. Additionally, consider installing fire sprinkler systems or fire extinguishers to provide a first line of defense against fires. Regularly test these systems to ensure their proper functioning.
5. Educate and Train Individuals on Fire Safety
Proper education and training on fire safety measures play a crucial role in preventing wood combustion incidents. Conduct fire safety training sessions for individuals, emphasizing the importance of knowing how to respond in case of a fire emergency. Teach individuals how to use fire extinguishers correctly and develop evacuation plans for different scenarios. Regularly review and practice these plans to ensure everyone is prepared in case of a fire.
6. Adhere to Local Fire Codes and Regulations
It is essential to stay updated on local fire codes and regulations to ensure compliance and implement appropriate fire safety measures. Local authorities establish these codes to promote fire safety and prevent incidents. Familiarize yourself with the requirements specific to your area, including regulations on wood-burning appliances, storage, and emergency preparedness.
7. Conduct Fire Risk Assessments
Regularly assess the fire risks associated with wood combustion in your environment. Identify potential ignition sources, flammable materials, and any other fire hazards. Evaluate your fire safety measures and make necessary improvements based on the findings of the assessment. By conducting regular fire risk assessments, you can proactively address potential issues and reduce the likelihood of wood combustion incidents.
In summary, preventing wood combustion requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper storage and handling of wood, installation of fire-resistant materials, regular maintenance and inspection, utilization of smoke alarms and fire suppression systems, education and training on fire safety, adherence to local fire codes, and conducting fire risk assessments. Implementing these fire safety measures and precautions can significantly reduce the risk of wood combustion incidents and help protect lives and property.
Controlling Wood Combustion: Fireproofing Techniques and Materials
Wood is a versatile and widely used material in construction and various industries. However, its combustible nature poses a significant fire hazard. To mitigate the risks associated with wood combustion, various fireproofing techniques and materials have been developed. In this section, we will explore these methods in detail, discussing their effectiveness and applications.
1. Fire-Resistant Coatings
Fire-resistant coatings are specially formulated paints or sprays that can be applied to wood surfaces to enhance their fire resistance. These coatings create a barrier that slows down the spread of flames and reduces the release of toxic gases. They are typically classified based on their fire rating, which indicates their effectiveness in preventing fire spread.
Common types of fire-resistant coatings include intumescent paints and cementitious coatings. Intumescent paints swell when exposed to heat, forming a protective char layer that insulates the wood. Cementitious coatings, on the other hand, contain cement-like substances that resist heat and provide a barrier against flames.
Fire-resistant coatings are commonly used in commercial buildings, warehouses, and other structures where fire safety is a top priority.
2. Fire Retardant Treatments
Fire retardant treatments involve the application of chemicals to wood to reduce its flammability. These treatments work by inhibiting the spread of flames and delaying ignition. They can be applied to both raw or finished wood surfaces, providing long-lasting fire protection.
Retardant treatments can be categorized as pressure treatments or surface treatments. Pressure treatments involve impregnating the wood with fire retardant chemicals under high pressure, ensuring deep penetration and enhanced fire resistance. Surface treatments, on the other hand, are applied directly to the wood surface and provide a protective coating.
Fire retardant treated wood is commonly used in construction, particularly for interior applications such as wall partitions and ceilings.
3. Firestops and Firebreaks
Firestops and firebreaks are physical barriers designed to prevent the spread of fire through concealed spaces or gaps in a building’s structure. They are crucial for compartmentalizing a structure and limiting fire progression.
Firestops are typically made of fire-resistant materials such as fire-rated gypsum board, mineral wool, or intumescent strips. They are installed in wall cavities, floors, and ceilings to seal off any openings that could allow flames or smoke to pass through.
Firebreaks, on the other hand, are open spaces or non-combustible materials that create breaks in a building’s design. These breaks help prevent the direct spread of fire, allowing occupants more time to evacuate and firefighters to control the blaze.
4. Fireproof Building Materials
Advancements in technology have led to the development of fireproof building materials that offer enhanced fire resistance compared to traditional wood. These materials are designed to withstand high temperatures and minimize fire hazards.
One example is fireproof gypsum board, also known as drywall. It contains glass fibers and other additives that make it highly resistant to fire. Fireproof glass is another innovative material that can withstand intense heat and prevent fire from spreading.
In addition, fire-resistant insulation materials, such as rock wool or glass wool, can be used to improve the fire resistance of walls and roofs.
5. Fire Suppression Systems
Fire suppression systems play a crucial role in controlling wood combustion by quickly detecting and extinguishing fires. These systems include sprinklers, fire alarms, and other devices that activate in the presence of heat or smoke.
Sprinkler systems are widely used in commercial and residential buildings, releasing water or other fire-retardant agents to suppress flames. They are effective in preventing fire spread and providing vital time for evacuation.
Fire alarms are essential for early detection and alerting building occupants to the presence of fire. They can be interconnected with other fire suppression systems, facilitating a prompt response to fire incidents.
Summary
Controlling wood combustion is of paramount importance to ensure fire safety in various industries and structures. Fireproofing techniques and materials, such as fire-resistant coatings, fire retardant treatments, firestops and firebreaks, fireproof building materials, and fire suppression systems, play crucial roles in mitigating fire risks. By implementing these measures, the fire resistance of wood can be significantly enhanced, minimizing the potential for devastating fires and protecting lives and property.
FAQs
What temperature does wood combust at?
Wood combustion typically occurs around 300 to 600 degrees Celsius (572 to 1112 degrees Fahrenheit), depending on the type of wood and its moisture content. However, wood can smolder and release combustible gases at lower temperatures as well.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the temperature at which wood combusts can vary depending on various factors. However, on average, wood ignites and starts to burn at temperatures between 300 and 500 degrees Celsius (572 to 932 degrees Fahrenheit). This combustion process releases heat, light, and byproducts such as smoke and ash. It is important to note that the ignition point of wood can be influenced by factors such as moisture content, type of wood, and presence of accelerants. Understanding the temperature at which wood combusts is crucial for fire safety and proper handling of wood-burning appliances.
Wood combustion plays a significant role in various contexts, including firewood for heating, cooking, and industrial processes. With its renewable and sustainable nature, wood remains a valuable and versatile fuel source. However, it is vital to handle and use wood responsibly to prevent accidents, maintain air quality, and protect the environment. By being aware of the temperature range at which wood combusts and following safety guidelines, we can enjoy the benefits of wood while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.